Criterion B: Developing Ideas
In this stage you will be expected to:
i. develop design specifications, which clearly states the success criteria for the design of a solution
- The design specs should be measurable with a clear way on how the specs will be tested.
pages 1-2
pages 1-2
i) What is a design specification?A specification is a set of constraints, requirements and considerations for a solution: what the solution
must or must not have to be successful.
A specification is not a description of the outcome. It should demonstrate
that you understand the needs of the problem that you have identified.
Every aspect of a specification must be specific, measurable, achievable,
realistic and testable / Time bound (SMART).
The specification should be directly connected to your design brief.
Writing a specification can be a difficult job if the design brief is not well
researched and written. If a solution or design fails to meet an aspect of
the specification, it can be considered that it has not met the criteria for
success.
You will need to refer back to your specification throughout the project,
particularly when developing ideas and evaluating the solution.
must or must not have to be successful.
A specification is not a description of the outcome. It should demonstrate
that you understand the needs of the problem that you have identified.
Every aspect of a specification must be specific, measurable, achievable,
realistic and testable / Time bound (SMART).
The specification should be directly connected to your design brief.
Writing a specification can be a difficult job if the design brief is not well
researched and written. If a solution or design fails to meet an aspect of
the specification, it can be considered that it has not met the criteria for
success.
You will need to refer back to your specification throughout the project,
particularly when developing ideas and evaluating the solution.
Example: Game Product
Specification
|
Test
|
Game will be less than 1 MB in size
|
Install it in a computer the size in properties
|
Played by two players (Multiplayer game)
|
Allow two players to play simultaneously
|
The game 3 levels that will advance in complexity.
|
Play the game at each level time the duration it takes to complete a level and record the complexities.
|
ii. develop a range of feasible design ideas, which can be correctly interpreted by others.
Pages 6 - 7
Pages 6 - 7
- Develop a range of good quality designs and measure each of them against the design specs.
- Your description for each design should be detailed and clear and use captions on images or diagrams which are not clear.
- develop and use a wide variety of techniques to generate a wide range of distinctly different designs through 2D modelling that are easily interpreted by others
- annotate designs with sufficient detail to explain how they meet the requirements of the design specification and to explain design thinking
- evaluate designs against the specification to identify the most feasible solutions
- develop the most feasible solutions to create a final design through modelling that fully meets the requirements of the design specification
- For both digital and product design, a natural starting place when designing is with a pencil and sheet of paper, developing rough sketches of potential solutions.
You should focus on getting the basic building blocks of ideas sketched out in short, concentrated bursts. These initial ideas should focus on generating a range of different solutions to the problem. You should then identify which initial ideas should be developed further. This could be done through a range of strategies, including:
- further, more detailed sketches that start to develop ideas with direct reference to the specification
- detailed annotation that allows students to explore and communicate their own thinking through annotation.
A range is not quantifiable. The number of ideas you create depends on the complexity of the problem, age, level of experience and time. When students ask how many ideas they should generate, the simple answer is: as many as it takes to solve the problem and to develop a design that meets all of the design specifications.
When developing your design ideas, you must always be working towards the goal of designing a solution to the problem, for which the requirements have been defined through the design specification.
Therefore, you must work towards developing at least one design to meet the specification.
You should develop, or refine, every detail, including:
· the exact size and shape of individual components
A range is not quantifiable. The number of ideas you create depends on the complexity of the problem, age, level of experience and time. When students ask how many ideas they should generate, the simple answer is: as many as it takes to solve the problem and to develop a design that meets all of the design specifications.
When developing your design ideas, you must always be working towards the goal of designing a solution to the problem, for which the requirements have been defined through the design specification.
Therefore, you must work towards developing at least one design to meet the specification.
You should develop, or refine, every detail, including:
When developing your design ideas, you must always be working towards the goal of designing a solution to the problem, for which the requirements have been defined through the design specification.
Therefore, you must work towards developing at least one design to meet the specification.
You should develop, or refine, every detail, including:
· the exact size and shape of individual components
· the required and/or available materials
· how the components fit together to create the whole
· the required and/or available tools and equipment
· aesthetics (colour, texture, shape, form, line, balance, finish)
· how the user will interact with the solution
· aspects relating to safety and accessibility.
What is a feasible idea? A feasible idea is an idea you could successfully make independently in the given time, with your skills, and with the resources at your disposal.
Why is "annotation" important?
Examples of Game design Storyboards.
Why is "annotation" important?
Annotation is vital for you to communicate the thinking behind your ideas and how that thinking develops. This is why annotation is so important. Simply sketching ideas will not clearly communicate them, as other people looking at these ideas may not interpret them correctly.
iii. present the chosen design and justify its selection. Pages 1- 2
- State the chosen design.
- Provide detailed justification why the design was chosen.
- Suggest possible improvements to the chosen design.
- If possible show the chosen design with the improvements included as a final design.
iv. develop accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outline the requirements for the
a) Table of requirements.
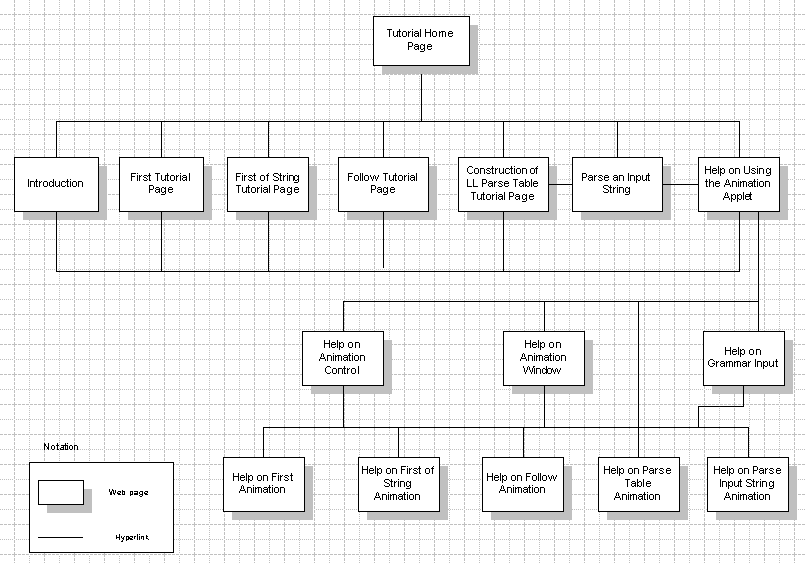
b) Flowchart
c) Site Map
b) Flowchart
c) Site Map
A. Table of requirements based on design specs/ .
B. Flowchart Symbols
Step
|
Task
|
Requirement/ Description
|
Resources/materials
|
1.
|
Signup to Wix
|
My Culture My Choice.
|
-internet
- Wix web builder
- computer
|
2.
|
Login to Wix account
|
|
- internet
- Wix web builder
- computer
|
B. Flowchart Symbols
checkout the following link for more on flow chart. http://www.smartdraw.com/flowchart/.of interest when interacting with the site above is the a) flowchart examples and b) flowchart symbols.
Take a case example of someone developing a database to:
i) capture records of books in the library
ii) register library users
iii) handle borrowing and returning of books
.
Sample flowcharts.
Animation / Video
Games
Apps/ CookBook
Magazine
C. Sitemap/ Layout
Sitemaps on the other hand explain the layout of your project. It would explain the various tables and the interconnection among the tables in the case of a database.
It explains the various pages and how they are linked in the case of a website, and so is the case for any other application.
Take a case example of the following website:
http://www.beachcampwatamu.com/
1. Magazines
2. Website
3. Apps
4. Games
5. Magazines
6. Video/ Animation
Criterion B Progress. Polling.
Assessment Criteria
Achievement level
|
Level descriptor
|
0
|
The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below.
|
1–2
|
The student:
i. lists some basic design specifications for the design of a solution
ii. presents one design, which can be interpreted by others
iii. creates incomplete planning drawings/diagrams.
|
3–4
|
The student:
i. lists some design specifications, which relate to the success criteria for the design of a solution
ii. presents a few feasible designs, using an appropriate medium(s) or annotation, which can be interpreted by others
iii. justifies the selection of the chosen design with reference to the design specification
iv. creates planning drawings/diagrams or lists requirements for the creation of the chosen solution.
|
5–6
|
The student:
i. develops design specifications, which outline the success criteria for the design of a solution
ii. develops a range of feasible design ideas, using an appropriate medium(s) andannotation, which can be interpreted by others
iii. presents the chosen design and justifies its selection with reference to the design specification
iv. develops accurate planning drawings/diagrams and lists requirements for the creation of the chosen solution.
|
7–8
|
The student:
i. develops detailed design specifications, which explain the success criteria for the design of a solution based on the analysis of the research
ii. develops a range of feasible design ideas, using an appropriate medium(s) and detailed annotation, which can be correctly interpreted by others
iii. presents the chosen design and justifies fully and critically its selection withdetailed reference to the design specification
iv. develops accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outlinesrequirements
|





















No comments:
Post a Comment